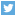Please come in if your child needs urgent medical attention. The sickest patients are always treated first and you may not be seen in the order of arrival. These numbers show the patients currently waiting and DO NOT predict how long your wait will be. When the emergency department is busy, patients with less urgent needs may have much longer wait times.
| What does the number of patients waiting mean? |
| This is the number of triaged patients who are waiting to be seen by a physician. This number includes patients in the waiting room and emergency department treatment rooms. This number does not include patients waiting in line to be triaged. |
| What does the expected longest wait for lower urgency patients mean? |
| This shows the expected longest wait for lower urgency patients arriving at this hour of day, based on recent data. This does not predict what your wait will be. You may wait longer if sicker patients need care. |
Does your child or youth need emergency care?
As a parent or guardian, you know your child best. CHEO’s Emergency Department is always here for you. Here are some examples to help you decide if your child is in need of emergency care.
 Emergency:
Emergency:
- Fever in infants less than 3 months old; children with immune system problems or complex chronic health problems; child is very sleepy or difficult to wake despite fever medicine
- Breathing problems including respiratory distress (working hard to breathe, breathing faster than normal, pale skin, whiteish or blue lips); asthma or wheezing not responding to usual puffers
- Vomiting or diarrhea in infants less than 3 months, child with repeated vomiting and unable to keep any liquids down for more than 8 hours, vomiting or diarrhea containing large amount of blood, signs of dehydration with dry mouth or no urine more than 8 hours
- Injuries such as:
- head injury with severe headache, loss of consciousness (passing out), confusion or repeated vomiting
- cuts that may need stitches, bleeding that won't stop
- burns that blister and are larger than a Loonie
- injury to arm or leg causing large swelling or inability to use the limb, obviously broken or dislocated bones
- eye injuries
- injury causing chest or stomach pain.
- Rash with fever that looks like tiny or expanding bruises
- Sudden weakness or difficulty talking
- Severe abdominal pain
 Not an emergency:
Not an emergency:
- Fever in healthy and vaccinated babies and children who appear generally well and playful when the fever is down with ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®) or acetaminophen (Tylenol®, Tempra®). Most fever in children is due to viral infection and lasts 3-5 days
- Symptoms of the 'common cold' including nasal congestion and cough (even if it interrupts sleep), mild asthma or wheezing that responds to usual puffers
- Vomiting or diarrhea less than 3-4 times a day if child is peeing well; ongoing diarrhea from the ‘stomach flu’ can last for up to two weeks.
- Injuries such as:
- minor head injuries (with no loss of consciousness, no confusion and no vomiting)
- scrapes and bruises where the injured part can still be used
- Sprained ankle if child is still able to walk, even if limping
- Recurring rashes or skin problems; rashes with cough and cold symptoms if the child looks well, mild hives without difficulty breathing or throat/ tongue swelling.
For more information to help you decide if your child or youth needs to visit the Emergency Department, read through this handout.
Alternatives to the Emergency Department
Find alternative options to the Emergency Department including walk-in and care clinics here